
Why is health insurance so expensive in the US? It’s a question that plagues many Americans, who often struggle to afford the rising costs of healthcare. The US healthcare system is unique in its complexity, with a combination of public and private insurance plans, intricate pricing structures, and a range of factors driving up expenses. From administrative overhead to pharmaceutical costs, the cost of healthcare in the US is significantly higher than in other developed countries.
This article explores the multifaceted reasons behind the high cost of health insurance in the US, examining the roles of government regulations, insurance company practices, and the broader healthcare landscape. We’ll delve into the impact of these factors on individuals and families, highlighting the financial burden and access challenges they face. Finally, we’ll explore potential solutions aimed at reducing healthcare costs and improving affordability.
The Rising Cost of Healthcare: Why Is Health Insurance So Expensive In The Us

The cost of healthcare in the United States has been steadily increasing for decades, becoming a significant burden for individuals, families, and the nation as a whole. Understanding the factors driving this rise is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Factors Contributing to Rising Healthcare Costs
The increasing cost of healthcare in the US is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including administrative inefficiencies, rising pharmaceutical costs, technological advancements, an aging population, and a lack of transparency in pricing.
Administrative Costs
Administrative costs associated with healthcare, such as billing, insurance processing, and paperwork, represent a significant portion of overall healthcare spending. The US healthcare system is characterized by a complex web of insurance plans, providers, and payers, leading to significant administrative burdens.
Pharmaceutical Costs
The cost of prescription drugs has been rising at an alarming rate, contributing substantially to the overall increase in healthcare spending. This rise is attributed to factors such as research and development costs, patent protection, and limited price negotiation.
Technology Advancements
While technological advancements have led to improved healthcare outcomes, they have also contributed to rising costs. Advanced medical imaging, sophisticated treatments, and complex surgeries often come with higher price tags.
Aging Population
As the US population ages, the demand for healthcare services increases, contributing to rising costs. Older individuals tend to have more chronic health conditions, requiring more frequent and expensive care.
Lack of Transparency in Pricing
A lack of transparency in healthcare pricing makes it difficult for patients to understand and compare costs, hindering their ability to make informed decisions. The opaque nature of pricing practices can contribute to higher costs.
Healthcare Spending Trends
Healthcare spending in the US has been steadily increasing over the past decade. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), national health expenditures reached $4.3 trillion in 2021, representing 19.7% of the nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
“National health expenditures are projected to grow at an average annual rate of 5.4% from 2022 to 2031.” – CMS
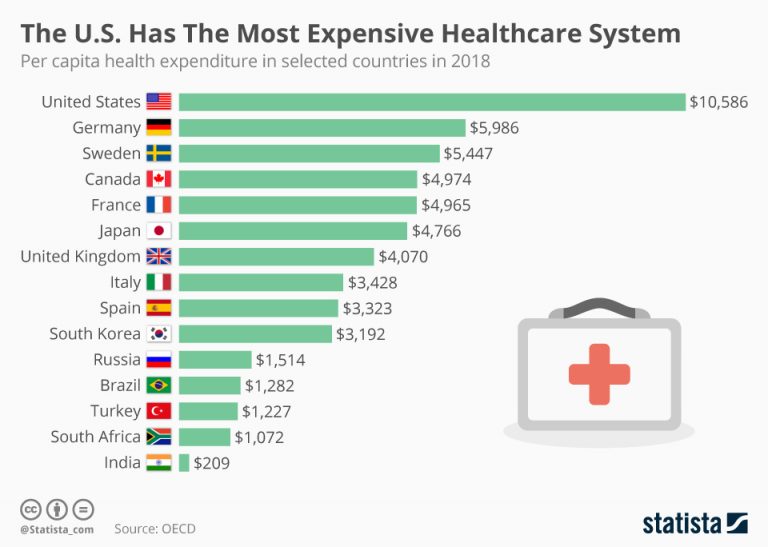
US Healthcare Spending Compared to Other Developed Nations
The US spends significantly more on healthcare than other developed nations, despite having lower life expectancy and higher rates of chronic diseases. This disparity highlights the need for reforms to improve efficiency and affordability.
“The United States spends more on healthcare than any other developed country, yet its health outcomes are worse than many other countries.” – Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
The Role of Health Insurance in the US Healthcare System
Health insurance plays a crucial role in the US healthcare system, acting as a financial intermediary between individuals and healthcare providers. It helps manage the costs of healthcare services, provides access to a wider range of medical options, and mitigates financial risks associated with unexpected health events.
Types of Health Insurance Plans in the US
The US offers a variety of health insurance plans, each with its own coverage, cost, and eligibility requirements. The most common types of health insurance plans include:
- Employer-Sponsored Plans: These plans are offered by employers to their employees and are typically the most common type of health insurance in the US. They are often more affordable than individual plans due to the economies of scale and tax advantages.
- Individual Plans: These plans are purchased directly by individuals, often through online marketplaces or insurance brokers. They offer more flexibility in choosing coverage but can be more expensive than employer-sponsored plans.
- Government-Sponsored Plans: These plans are offered by the government to specific populations, such as seniors, low-income individuals, and people with disabilities. They include:
- Medicare: A federal program that provides health insurance for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger people with disabilities.
- Medicaid: A joint federal and state program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families.
Health Insurance Company Operations
Health insurance companies operate by collecting premiums from their policyholders and using those funds to pay for the healthcare costs of their members. They generate revenue through:
- Premiums: Regular payments made by policyholders for coverage.
- Investment Income: Returns earned from investing premium funds.
Health insurance companies aim to maintain a certain profit margin to cover their operating expenses and ensure financial stability. Their profit margins are typically lower than other industries due to the highly regulated nature of the healthcare market and the unpredictable nature of healthcare costs.
Components of Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are typically calculated based on a variety of factors, including age, health status, location, and coverage level. They are comprised of several components, including:
- Co-pays: Fixed amounts paid by policyholders for specific services, such as doctor’s visits or prescriptions.
- Deductibles: The amount policyholders must pay out-of-pocket before their insurance coverage kicks in.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximums: The maximum amount policyholders are required to pay out-of-pocket in a given year, after which their insurance covers all remaining healthcare costs.
Factors Contributing to High Health Insurance Premiums
The cost of health insurance in the United States is a complex issue with numerous contributing factors. These factors are interconnected and can influence each other, leading to a challenging situation for both individuals and the healthcare system as a whole.
Impact of Pre-existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions, which are health issues an individual has before obtaining health insurance, significantly impact premiums. Insurance companies consider pre-existing conditions as higher risks, as individuals with these conditions are more likely to require healthcare services. To account for this increased risk, insurance companies often charge higher premiums to individuals with pre-existing conditions. This practice can make it challenging for individuals with pre-existing conditions to afford comprehensive health insurance, potentially leading to a cycle of limited access to care and higher healthcare costs in the long run.
Role of Risk Pools
Risk pools are groups of individuals who are insured together. Insurance companies use risk pools to spread the risk of healthcare costs across a larger population. Individuals in a risk pool with a higher proportion of healthy individuals tend to have lower premiums, as the cost of healthcare is spread across more people. Conversely, risk pools with a higher proportion of individuals with pre-existing conditions or those who utilize healthcare services more frequently will have higher premiums. The composition of risk pools is influenced by various factors, including demographics, geographic location, and the availability of affordable health insurance options.
Factors Influencing Individual Health Insurance Premiums
A variety of factors influence individual health insurance premiums. These factors are considered by insurance companies when calculating individual premiums, ensuring that premiums reflect the risk associated with each individual.
- Age: Older individuals tend to have higher health insurance premiums because they are statistically more likely to require healthcare services. As individuals age, they are more susceptible to chronic illnesses and health conditions, leading to increased healthcare utilization and costs.
- Location: Health insurance premiums can vary based on location. The cost of living, availability of healthcare providers, and the prevalence of certain health conditions in a particular area can influence premiums. For example, premiums may be higher in areas with a higher concentration of specialists or in areas with a higher cost of living.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing conditions or those who have a history of high healthcare utilization tend to have higher premiums. Insurance companies assess health status through medical history, health screenings, and other factors to determine the potential risk associated with insuring an individual.
- Coverage Level: The level of coverage selected by an individual also influences premiums. Individuals with higher coverage levels, such as those with comprehensive plans that cover a wider range of services, will typically have higher premiums compared to individuals with more limited coverage.
Impact of Government Regulations and Mandates
Government regulations and mandates, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA), can influence health insurance premiums. The ACA implemented regulations aimed at expanding access to health insurance and making it more affordable. These regulations, including the individual mandate, which required individuals to have health insurance or pay a penalty, have had a significant impact on the health insurance market. The ACA also introduced provisions related to pre-existing conditions, requiring insurance companies to cover individuals regardless of their health status. These regulations have influenced the composition of risk pools and the cost of health insurance, with some argue that they have led to higher premiums for some individuals.
The Impact of High Health Insurance Costs on Individuals and Families

The high cost of health insurance in the United States poses a significant financial burden on individuals and families, impacting their financial well-being and access to healthcare. Rising premiums and deductibles often leave individuals struggling to afford essential medical care, leading to a cascade of negative consequences.
Financial Burden of High Premiums
High health insurance premiums represent a substantial financial burden for many Americans. The average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance in 2022 was $7,739 for single coverage and $22,221 for family coverage, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. These costs can consume a significant portion of an individual’s or family’s income, leaving less money available for other essential expenses like housing, food, and education.
Consequences of High Healthcare Costs
Medical Debt
The high cost of healthcare often leads to medical debt. Many individuals and families struggle to pay their medical bills, resulting in unpaid balances that can accumulate over time. According to a 2021 report by the Kaiser Family Foundation, approximately 1 in 5 adults in the United States have medical debt. This debt can lead to a cycle of financial hardship, as individuals may be forced to choose between paying for essential medical care and meeting other financial obligations.
Delayed or Forgone Care
The fear of incurring high medical expenses can lead individuals to delay or forgo necessary healthcare. A 2019 study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that nearly one in four adults in the United States had delayed or avoided medical care due to cost concerns. This can have serious consequences for their health, as early detection and treatment of medical conditions are often more effective and less costly in the long run.
Financial Hardship
High healthcare costs can contribute to financial hardship, leading to stress, anxiety, and even bankruptcy. A 2018 study by the American Medical Association found that medical debt was a significant factor in approximately 665,000 personal bankruptcies in the United States. The financial strain of high healthcare costs can also lead to a decline in overall well-being, as individuals may struggle to maintain a stable financial situation and meet their basic needs.
Impact on Access to Healthcare Services
High health insurance premiums can significantly impact access to healthcare services. Individuals with limited financial resources may find it difficult to afford comprehensive health insurance coverage, limiting their access to essential medical care. This can exacerbate health disparities and lead to poorer health outcomes for those who are already most vulnerable.
Potential Solutions to Address High Health Insurance Costs
The high cost of health insurance in the US is a significant issue affecting individuals, families, and the overall economy. While the factors contributing to these costs are complex, there are potential solutions that could help alleviate the burden on Americans. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving government policies, industry reforms, and individual behavioral changes.
Negotiating Lower Drug Prices
The high cost of prescription drugs is a major driver of healthcare expenses. One potential solution is to negotiate lower drug prices. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as:
- Allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices: Currently, Medicare is prohibited from negotiating drug prices with pharmaceutical companies. Allowing Medicare to negotiate would leverage its vast purchasing power to secure lower prices for a significant portion of the population.
- Importing prescription drugs from Canada: Importing drugs from Canada, where prices are often lower, could increase competition and drive down prices in the US. However, there are regulatory hurdles and concerns about safety that need to be addressed.
- Promoting generic drug use: Encouraging the use of generic drugs, which are often significantly cheaper than brand-name medications, can help reduce overall drug costs.
Promoting Transparency in Healthcare Pricing
Lack of transparency in healthcare pricing contributes to higher costs. Patients often have limited information about the cost of procedures, tests, and medications, making it difficult to compare prices and negotiate better rates.
- Requiring hospitals and providers to publish price lists: Making price information publicly available would empower consumers to make informed decisions and potentially negotiate lower prices.
- Encouraging price comparison tools: Developing online tools that allow patients to compare prices for various healthcare services would promote competition and transparency.
- Promoting price transparency in insurance plans: Requiring insurance companies to provide clear and understandable information about the cost of coverage and out-of-pocket expenses would enable consumers to make more informed choices.
Implementing Cost-Sharing Mechanisms
Cost-sharing mechanisms, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, can encourage individuals to be more mindful of their healthcare spending. However, it’s crucial to ensure that these mechanisms are implemented fairly and do not disproportionately burden low-income individuals.
- Promoting high-deductible health plans (HDHPs): HDHPs offer lower premiums but require individuals to pay a higher deductible before insurance coverage kicks in. This can encourage cost-consciousness and promote preventive care.
- Expanding access to health savings accounts (HSAs): HSAs allow individuals to save pre-tax money for healthcare expenses, potentially reducing out-of-pocket costs.
- Designing cost-sharing mechanisms that are sensitive to income: Implementing cost-sharing mechanisms that are tailored to individuals’ income levels could help ensure that healthcare costs are affordable for all.
Expanding Access to Preventive Care
Preventive care, such as regular checkups, screenings, and vaccinations, can help prevent chronic diseases and reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
- Eliminating cost-sharing for preventive services: Removing copayments and deductibles for preventive services would encourage individuals to access these services more frequently.
- Expanding access to preventive care programs: Providing more comprehensive preventive care programs, such as community health centers and mobile clinics, would ensure that preventive services are accessible to all.
- Promoting healthy lifestyle choices: Encouraging healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and smoking cessation, can reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases and lower healthcare costs.
Encouraging Healthy Lifestyles, Why is health insurance so expensive in the us
Promoting healthy lifestyles through education, awareness campaigns, and access to resources can help prevent chronic diseases and reduce healthcare costs.
- Investing in public health initiatives: Supporting programs that promote healthy eating, physical activity, and smoking cessation can help improve overall health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
- Encouraging healthy food choices: Implementing policies that promote access to healthy food options, such as subsidies for farmers markets and healthy school lunches, can encourage healthier dietary choices.
- Creating walkable and bikeable communities: Designing communities that encourage walking and biking can promote physical activity and reduce reliance on cars, leading to improved health outcomes.
Comparing Policy Proposals
| Policy Proposal | Pros | Cons |
|—|—|—|
| Allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices | Lower drug prices for Medicare beneficiaries, potentially leading to lower overall healthcare costs. | Potential impact on drug innovation, as pharmaceutical companies may invest less in research and development. |
| Importing prescription drugs from Canada | Lower drug prices for consumers, increased competition in the pharmaceutical market. | Concerns about safety and regulatory hurdles, potential impact on US pharmaceutical industry. |
| Promoting generic drug use | Lower drug prices for consumers, increased competition in the pharmaceutical market. | Potential for lower quality generic drugs, lack of awareness about generic drug options. |
| Requiring hospitals and providers to publish price lists | Increased transparency in healthcare pricing, empowering consumers to make informed decisions. | Potential for complex pricing structures, challenges in comparing prices across different providers. |
| Encouraging price comparison tools | Increased transparency in healthcare pricing, empowering consumers to make informed decisions. | Potential for limited availability of price comparison tools, challenges in collecting accurate price data. |
| Promoting price transparency in insurance plans | Increased transparency in insurance plans, empowering consumers to make informed decisions. | Potential for complex insurance plan designs, challenges in understanding coverage details. |
| Promoting high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) | Lower premiums, encouraging cost-consciousness and preventive care. | Higher out-of-pocket costs for individuals, potential for delaying or forgoing necessary care. |
| Expanding access to health savings accounts (HSAs) | Tax advantages for healthcare savings, potential for reducing out-of-pocket costs. | Limited access for low-income individuals, potential for misuse of funds. |
| Designing cost-sharing mechanisms that are sensitive to income | Ensuring that healthcare costs are affordable for all. | Complex implementation, potential for administrative burdens. |
| Eliminating cost-sharing for preventive services | Encouraging individuals to access preventive services more frequently, potentially reducing healthcare costs in the long run. | Potential for increased utilization of preventive services, leading to higher overall healthcare costs. |
| Expanding access to preventive care programs | Ensuring that preventive services are accessible to all. | Potential for limited funding and resources, challenges in reaching underserved populations. |
| Investing in public health initiatives | Improving overall health outcomes, reducing healthcare costs in the long run. | Potential for long-term investments, challenges in measuring impact. |
| Encouraging healthy food choices | Promoting healthier dietary choices, potentially reducing healthcare costs. | Potential for unintended consequences, such as increased food prices or reduced access to affordable food options. |
| Creating walkable and bikeable communities | Promoting physical activity, potentially reducing healthcare costs. | Potential for high infrastructure costs, challenges in adapting existing communities. |
Final Conclusion
The high cost of health insurance in the US is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, understanding the factors driving these costs is crucial for informed policy decisions and individual financial planning. By exploring the roles of administrative costs, pharmaceutical pricing, and the broader healthcare landscape, we can identify potential avenues for improvement. Ultimately, the goal is to create a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system that provides affordable access to quality care for all Americans.
Clarifying Questions
Why are prescription drugs so expensive in the US?
Several factors contribute to high drug prices in the US, including limited price negotiation, a lack of generic competition, and the high cost of research and development. Additionally, direct-to-consumer advertising and marketing play a role in driving up demand and prices.
How do insurance companies make money?
Health insurance companies generate revenue primarily through premiums paid by individuals and employers. They use these premiums to cover healthcare costs incurred by their policyholders, as well as administrative expenses and profit margins. Insurance companies also invest a portion of their premiums to generate returns.
What are some ways to lower my health insurance premiums?
Several strategies can help lower health insurance premiums, such as shopping around for different plans, choosing a higher deductible, and considering a health savings account (HSA). Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and getting regular checkups can also reduce your risk and potentially lower premiums.
