
ACV car insurance, also known as actual cash value insurance, is a type of coverage that pays out the fair market value of your vehicle at the time of a total loss. Unlike other types of car insurance that aim to replace your vehicle with a new one, ACV insurance considers depreciation, meaning you’ll receive the value of your car minus its accumulated depreciation. This type of coverage is often chosen by individuals who are looking for more affordable car insurance premiums, as it generally costs less than replacement value coverage.
Understanding how ACV is calculated and its implications is crucial for making informed decisions about your car insurance. Several factors influence the determination of ACV, including the vehicle’s make, model, year, mileage, condition, and current market value. Depreciation plays a significant role in this calculation, and the older your vehicle is, the lower its ACV will be. It’s essential to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of ACV coverage before deciding if it’s the right choice for you.
ACV Car Insurance Explained
ACV car insurance is a type of coverage that pays out the actual cash value of your vehicle in the event of a total loss. This means that the insurance company will pay you the fair market value of your car, which is typically determined by its age, condition, mileage, and other factors.
ACV car insurance is different from other types of car insurance, such as replacement cost coverage, which pays out the full cost of replacing your vehicle with a new one. ACV insurance is typically less expensive than replacement cost coverage, but it also provides less financial protection.
When ACV Car Insurance is Suitable
ACV car insurance can be a good option for drivers who:
- Own older vehicles: The value of older vehicles depreciates quickly, so ACV insurance may be a more affordable option than replacement cost coverage.
- Have a limited budget: ACV insurance premiums are generally lower than replacement cost coverage premiums, making it a more affordable option for drivers on a tight budget.
- Are comfortable with receiving the fair market value of their vehicle: If you are not concerned about getting the full cost of a new vehicle, ACV insurance may be a good option for you.
How ACV is Calculated
Understanding how ACV is calculated is crucial for policyholders, as it determines the amount of compensation they receive in case of a total loss. The ACV is calculated by considering several factors that influence the value of the vehicle, primarily taking into account depreciation.
Depreciation
Depreciation is the decrease in value of an asset over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or market factors. Depreciation is a significant factor in determining ACV, as it reflects the vehicle’s current market value. As vehicles age, they depreciate in value, meaning the ACV will be lower than the original purchase price.
Depreciation can be calculated using various methods, such as straight-line depreciation, declining balance depreciation, or sum-of-the-years’ digits depreciation.
The specific depreciation method used may vary depending on the insurer and the vehicle’s age and condition. However, the principle remains the same: the older and more used a vehicle is, the lower its ACV will be.
Factors Influencing ACV Calculation
Several factors are considered when calculating ACV. These factors, besides depreciation, are:
- Vehicle’s Make and Model: Popular models with higher demand tend to retain value better than less popular models.
- Mileage: Higher mileage generally indicates more wear and tear, leading to lower ACV.
- Condition: Vehicles in good condition with proper maintenance will have a higher ACV than those with damage or neglect.
- Location: The geographical location can affect the demand for specific vehicles, influencing their ACV.
- Market Value: Insurers use various sources, such as Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds, to determine the current market value of similar vehicles. This value is used as a benchmark for calculating ACV.
Estimating ACV
While insurers ultimately determine the ACV, policyholders can estimate their vehicle’s potential ACV using online tools or resources. Some popular tools include:
- Kelley Blue Book (KBB): KBB provides estimated values for new and used vehicles based on various factors, including make, model, year, mileage, condition, and location.
- Edmunds: Edmunds offers similar valuation services as KBB, providing estimated values for vehicles based on various factors.
- NADA Guides: NADA Guides provides comprehensive valuation data for new and used vehicles, including ACV estimates.
It is important to note that these online tools provide estimates, and the actual ACV determined by the insurer may differ. However, these tools can provide a good starting point for understanding your vehicle’s potential value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ACV Car Insurance

Choosing the right car insurance coverage can be a crucial decision. While many opt for comprehensive coverage, ACV (Actual Cash Value) car insurance presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these aspects is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with your needs and financial situation.
Benefits of ACV Car Insurance
ACV car insurance offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for certain individuals.
- Lower Premiums: One of the most significant advantages of ACV car insurance is its lower premiums compared to other types of coverage. Since it only covers the vehicle’s current market value, insurers have less financial risk, leading to more affordable premiums.
- Suitable for Older Vehicles: ACV car insurance is particularly advantageous for owners of older vehicles with lower market values. As the car depreciates over time, the cost of comprehensive coverage may become disproportionate to the vehicle’s worth. In such cases, ACV insurance provides a more economical option.
- Focus on Basic Protection: ACV insurance prioritizes basic coverage, ensuring that you are protected against liability claims and potential damages to other vehicles. It provides essential financial protection without the added cost of comprehensive coverage.
Potential Drawbacks of ACV Coverage
While ACV car insurance offers certain benefits, it also comes with potential drawbacks that you should consider.
- Limited Coverage: ACV insurance only covers the vehicle’s current market value, meaning you will not receive enough to replace your car if it is totaled or stolen. The payout will reflect the car’s depreciated value, not its original purchase price.
- Lack of Coverage for Specific Events: ACV insurance typically does not cover certain events, such as floods, earthquakes, or vandalism. Comprehensive coverage is often required for such incidents.
- Uncertainty in Value Determination: The determination of a vehicle’s current market value can be subjective and may vary depending on the insurer’s assessment. This can lead to potential disagreements regarding the payout amount.
Comparison with Other Car Insurance Options
ACV car insurance is often compared to other options, such as comprehensive coverage and gap insurance.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Comprehensive coverage offers broader protection than ACV insurance, covering a wider range of events, including theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. However, it comes with higher premiums.
- Gap Insurance: Gap insurance bridges the difference between the vehicle’s actual cash value and the outstanding loan balance. This coverage is beneficial for those who have financed their vehicles, as it ensures they are not left with debt after a total loss.
ACV Car Insurance for Different Vehicle Types
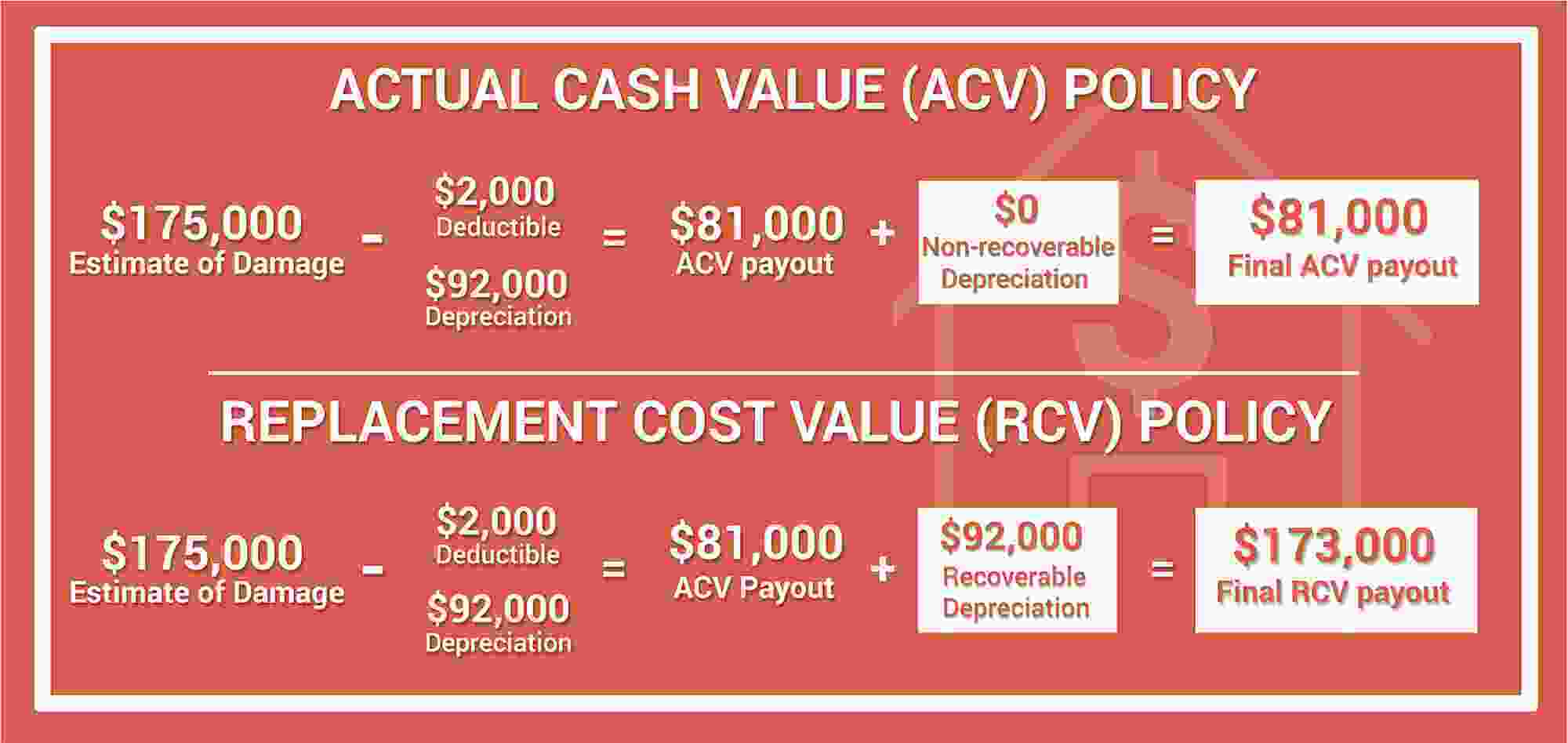
ACV, or Actual Cash Value, is calculated differently for various vehicle types. Factors like age, condition, and market value play a crucial role in determining the ACV for a car. This section explores how ACV is applied to different vehicle types and how the calculation might vary based on factors like age and condition.
ACV for Classic Cars
Classic cars are often considered valuable assets and are often insured with collector car insurance. The ACV for a classic car is typically based on its market value, which is determined by its condition, rarity, and historical significance. In some cases, classic cars might be insured for a higher value than their current market value if they have been restored or have unique features that increase their desirability.
ACV for New Cars
New cars are generally valued at their MSRP (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price) minus depreciation. The depreciation rate for new cars is typically higher in the first few years, and then it slows down over time. This means that the ACV for a new car will decrease rapidly in the first few years, but it will then level off.
For example, a new car that costs $30,000 might have an ACV of $25,000 after one year, $20,000 after two years, and $15,000 after three years.
ACV for Used Cars
Used cars are typically valued based on their age, mileage, condition, and market value. The ACV for a used car will generally be lower than the MSRP of a new car of the same model. The depreciation rate for used cars is generally slower than for new cars, but it will still decrease over time.
For example, a used car that was purchased for $15,000 might have an ACV of $12,000 after one year, $10,000 after two years, and $8,000 after three years.
ACV for Vehicles in Different Conditions
The condition of a vehicle also plays a significant role in determining its ACV. A vehicle in excellent condition will typically have a higher ACV than a vehicle in poor condition. Factors that affect the condition of a vehicle include:
- Body damage
- Engine condition
- Interior condition
- Maintenance records
For example, a used car with minor body damage might have an ACV that is 10% lower than a car in excellent condition.
Choosing the Right Car Insurance for Your Needs
Deciding on the best car insurance for your situation involves understanding your needs and priorities. While ACV car insurance might be a cost-effective option for some, it’s essential to weigh its pros and cons carefully. This section will guide you through the process of selecting the right car insurance coverage, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Car Insurance Coverage
Choosing the right car insurance involves evaluating various factors that affect your coverage and premiums. Understanding these factors empowers you to make a decision that aligns with your specific needs and financial situation.
- Your Vehicle’s Value: ACV insurance is typically more suitable for older vehicles with lower market values. If your car is newer or has significant sentimental value, consider a policy that provides replacement cost coverage.
- Your Driving History: A clean driving record can qualify you for lower premiums. Maintaining a safe driving habit can significantly impact your insurance costs.
- Your Budget: Set a realistic budget for your car insurance premiums. Compare different policies and coverage options to find the best value within your financial constraints.
- Your Location: The geographic location where you reside can influence insurance premiums. Factors like population density, crime rates, and weather conditions can impact pricing.
- Your Driving Habits: Consider your typical driving patterns, including mileage, commute distance, and driving frequency. If you drive less often or for shorter distances, you might qualify for discounts.
Comparing Insurance Quotes and Policies
Once you’ve considered the factors above, it’s time to shop around for insurance quotes. Comparing different policies from various insurers can help you find the best coverage at a competitive price.
- Get Multiple Quotes: Contact several insurance companies to obtain quotes for different coverage options. Use online comparison tools or work with an insurance broker to streamline the process.
- Compare Coverage Details: Carefully review each quote, paying attention to the specific coverage details, deductibles, and limits. Understand the differences in coverage provided by each policy.
- Consider Discounts: Inquire about available discounts, such as safe driver discounts, multi-car discounts, and good student discounts. These can significantly reduce your premium.
- Read Policy Documents: Before finalizing your choice, carefully read the policy documents to understand the terms and conditions. Ensure you are comfortable with the coverage and exclusions.
Summary

Choosing the right car insurance coverage is a critical decision that requires careful consideration. While ACV car insurance can be a cost-effective option for some individuals, it’s important to understand its limitations. By carefully assessing your individual needs, comparing different insurance policies, and seeking expert advice, you can make an informed choice that provides the right level of protection for your vehicle.
FAQ Resource
What are some examples of scenarios where ACV car insurance is suitable?
ACV car insurance is generally suitable for older vehicles with lower market values. If your car is worth less than the cost of a new one, ACV coverage might be a more affordable option. It can also be a good choice for individuals who are looking to save money on their insurance premiums.
How often is ACV recalculated?
ACV is typically recalculated at the time of a claim. The insurance company will use various resources and data to determine the fair market value of your vehicle based on its condition, mileage, and current market value at the time of the loss.
Can I choose to have ACV coverage on a new car?
Yes, you can choose to have ACV coverage on a new car, but it’s generally not recommended. Since new cars depreciate quickly, you’ll receive significantly less money for a total loss than if you had replacement value coverage.
